Team Nicola MARCHI – Étienne AUDINAT
Cerebrovascular and Glia Research


We examine cells within the neurovascular unit in the context of central nervous system diseases. Through translational research, we explore how neurovascular cells’ responsiveness and adaptability and the blood-brain barrier’s permeability influence neuroinflammation, exacerbating changes in neuronal function over time. Our approach integrates in vivo and in vitro laboratory studies with clinical investigations to understand the underlying mechanisms and assess peripheral blood biomarkers associated with dysfunction in the neurovascular unit.
Glio-vascular cell reactivity in experimental and human focal and genetic epilepsies. This framework is relevant for cases where seizures cannot be adequately controlled with anti-seizure medications or where, regardless of drug responsiveness, side effects must be minimized. We integrate cellular-level and neurophysiological tools, in vitro and preclinical models (including status epilepticus, temporal lobe epilepsy, and Dravet syndrome), and the analysis of surgically resected human brain tissue to investigate the role of glial cell reactivity and blood-brain barrier damage in the pathophysiology of these seizure conditions. We explore opportunities for novel targets and the discovery of blood or imaging biomarkers to improve patient management. Our research also examines the contribution of seizures to neurological deficits and neurodegeneration in the aging population.
Neurovascular damage and immune communications in human stroke. The goal of our research is to identify specific molecular and biomarker signatures that can inform the development of add-on therapeutic options, which would target key inflammatory pathways in conjunction with mechanical thrombectomy. By focusing on these inflammatory pathways, we aim to not only enhance the effectiveness of mechanical thrombectomy but also reduce the risk of post-procedural complications and improve patient outcomes. Our clinical team leverages mechanical thrombectomy procedures to obtain intracranial clot and peri-clot blood samples. These samples are analyzed to characterize the inflammatory milieu within the affected tissue and surrounding vasculature. This enables us to improve our understanding of the molecular et cellular mechanisms involved.
Environmental contaminants and xenobiotics at brain borders: risk factors of neuro-inflammation and neuro-vascular frailty. The impact of exposure to environmental pollutants or xenobiotics on neuro-glio-vascular structures and cells remains unclear. We investigate the effects of long-term, age-related exposure to contaminants at realistic doses on CNS functions and peripheral organs. Given that perinatal inflammation, primarily driven by the reactivity of glial and vascular cells, is a known risk factor for the development of neurological and psychiatric disorders, a critical aspect of our project is to evaluate the consequences of contaminant exposure (pesticides, bisphenol and others) during embryonic and postnatal development on glia and cerebrovascular cells in adulthood.
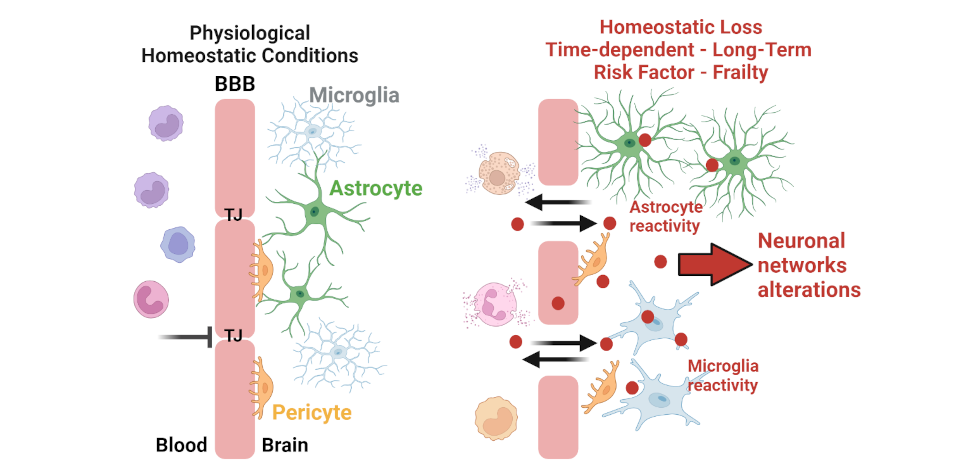
The Neurovascular Unit: A Nexus in CNS Diseases and Maladaptation. At the NVU, the blood-brain barrier (BBB) consists of a tight endothelial-pericyte-astrocyte end-feet assembly. In response to acute insults or chronic conditions (peripheral or brain), BBB permeability increases with pericyte and glial cell reactivity. These events contribute to a loss of parenchymal homeostasis and facilitate aberrant synaptic transmission, thereby representing a risk factor for negative neurological sequelae and brain frailty.

 IGF Sud 215
IGF Sud 215 04 34 35 92 09
04 34 35 92 09
 IGF Sud 118
IGF Sud 118 04 34 35 92 20
04 34 35 92 20
 IGF Nord 013
IGF Nord 013 04 11 75 96 80
04 11 75 96 80
 IGF Sud 118
IGF Sud 118 04 34 35 92 20
04 34 35 92 20
 IGF Sud 118
IGF Sud 118 04 34 35 92 20
04 34 35 92 20
 IGF Sud 118
IGF Sud 118 04 34 35 92 20
04 34 35 92 20
 IGF Sud 113
IGF Sud 113 04 34 35 92 20
04 34 35 92 20
 IGF Sud 118
IGF Sud 118 04 34 35 92 20
04 34 35 92 20
 IGF Sud 118
IGF Sud 118 04 34 35 92 20
04 34 35 92 20
 IGF Sud 118
IGF Sud 118 04 34 35 92 20
04 34 35 92 20
 IGF Sud 118
IGF Sud 118 04 34 35 92 20
04 34 35 92 20
 IGF Sud 116
IGF Sud 116 04 34 35 92 85
04 34 35 92 85
 IGF Sud 118
IGF Sud 118 04 34 35 92 20
04 34 35 92 20
 IGF Sud 118
IGF Sud 118 04 34 35 92 20
04 34 35 92 20
 IGF Sud 118
IGF Sud 118 04 34 35 92 20
04 34 35 92 20
 IGF Sud 215
IGF Sud 215 04 34 35 92 09
04 34 35 92 09- Nicole Pinzon-Hoyos, Yibo Li, Monnie McGee, Nicholas P Poolos, Nicola Marchi, Amy L Brewster. Drug-resistant epilepsy associated with peripheral complement decreases and sex-specific cytokine imbalances: a pilot study. Scientific Report, in press 2025
- Cyril Dargazanli#, Marine Blaquière , Marinette Moynier , Frédéric de Bock , Julien Labreuche, Adrien Ter Schiphorst, Imad Derraz, Răzvan Alexandru Radu, Gregory Gascou, Pierre Henri Lefevre, Francesca Rapido, Julien Fendeleur, Caroline Arquizan, Romain Bourcier, Philippe Marin, Paolo Machi, Federico Cagnazzo, Christophe Hirtz, Vincent Costalat#, Nicola Marchi#. Inflammation biomarkers in the intracranial blood are associated with outcome in patients with ischemic stroke. J Neurointerv Surg 2025 Jan 17;17(2):159-166. doi: 10.1136/jnis-2023-021365.
- V. Costalat et. al. Trial of Thrombectomy for Stroke with a Large Infarct of Unrestricted Size. N Engl J Med 2024 May 9;390(18):1677-1689. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2314063.
- Noemie Cresto, Laurent Givalois, Jerome Badaut, Alicia Janvier, Athenais Genin, Etienne Audinat, Amy L Brewster, Nicola Marchi Bursts of brain erosion: Seizures and age-dependent neurological vulnerability. Trends in Molecular Medicine, Dec, 2024
- Noemie Cresto, Margot Courret, Athénaïs Génin, Céline Marie, Pauline Martin, Julie Bourret, Sophie Sakkaki, Frederic de Bock, Alicia Janvier, Arnaud Polizzi, Laurence Payrastre, Sandrine Ellero-Simatos, Etienne Audinat, Julie Perroy, Nicola Marchi. Continuous low-level dietary exposure to glyphosate elicits dose and sex-dependent synaptic and microglial adaptations in the rodent brain. Environmental Pollution Volume 345, 15 March 2024, 123477
- Garcia V*, Blaquiere M*, Janvier A, Cresto N, Lana C, Genin A, Hirbec H, Audinat E, Faucherre A, Barbier EL, Hamelin S, Kahane P, Jopling C, Marchi PIEZO1 expression at the glio-vascular unit adjusts to neuroinflammation in seizure conditions. Neurobiology of Disease 2023. doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2023.106297.
- Erwin vanVliet and Nicola Marchi. Neurovascular unit dysfunction as a mechanism of seizures and epilepsy during aging. Epilepsia 2022. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.17210
- Canet G, Zub E, Zussy C, Hernandez C, Blaquiere M, Garcia V, Vitalis M, DeBock F, Moreno-Montano M, Audinat E, Desrumaux C, Planel E, Givalois L, Marchi N. Seizure activity triggers tau hyperphosphorylation and amyloidogenic pathways. Epilepsia 2022. doi: 10.1111/epi.17186
- Paolicelli RC et al., Microglia states and nomenclature: A field at its crossroads. Neuron 2022 10(21): 3458-3483 doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.10.020
- Forner-Piquer I, Faucherre A, Byram J, Blaquiere M, de Bock F, Gamet-Payrastre L, Ellero-Simatos S, Audinat E, Jopling C, Marchi N. Differential impact of dose-range glyphosate on locomotor behavior, neuronal activity, glio-cerebrovascular structures, and transcript regulations in zebrafish larvae. Chemosphere 2021 267:128986. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128986.
- Thion MS*, Mosser CA*, Ferezou I, Grisel P, Baptista S, Low D, Ginhoux F, Garel S*, Audinat E*. Biphasic impact of prenatal inflammation and microglia depletion on the wiring of neocortical inhibitory circuits. Cell Reports 2019 30;28(5):1119-1126.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.06.086
Mechanisms of neurovascular damage and inflammation due to large vessel occlusion (V. Costalat, C. Dargazanli, A. Ter-Schiphorst, F. Cagnazzo, E. LeBars, CHU Montpellier/IGF). We investigate brain and systemic inflammatory or biomarker signatures in post-ischemic stroke using cardio-embolic and atherosclerotic human clots and intracranial blood samples. We aim to improve patient management and offer add-on therapeutic option along with mechanical thrombectomy. We study mechanisms of idiopathic intracranial hyper- or hypo-tension. Find out more
Analysis of explanted intracranial electrodes in drug-resistant epilepsy as a source of intracranial biological traces (Prof. Bartolomei, J. Scholly, S. Lagarde, CHU La Timone, Marseille). The goal is to isolate a nano-scale quantity of RNA or protein derived from the intracranial tissue environment where the depth electrode resided during the pre-surgical exploration of seizure networks. To overlap these innovative biological data with those obtained by imaging and SEEG to establish a map of the molecular physiological connections in the epileptic brain. Find out more
Neurovascular damage and inflammatory cross-talk in psychiatric conditions: focus on depression and suicide attempts (P. Courtet, E. Olie, R. Belzeaux; CHU/IGF). The goal is to discover outcome protein biomarkers in blood and to develop an add-on therapeutic option based on the modulation of specific inflammatory players.
- Garel (ENS Paris), N. Rouach (Collège de France, Paris) : Microglia in the wiring of Inhibitory circuits during sensory cortex critical periods (MicroSenso) ; ANR-19-CE16-0018
- Rassendren and P. Mollard teams (IGF) : Deciphering ATP Signaling in Epilepsy with Biosensors (Diapason) ; ANR-20-CE16-0003.
- Levi (IFM, Paris), D. Blum (Lille Neuroscience & Cognition), C. Bernard (INS Marseille) : The Janus-faced Impact of caffeine in the developing and the ageing brain: role of synaptic remodeling (JANUS) ; ANR-21-CE14-0053.
- Hirbec (Rassendren team, IGF), G. Dorothée (Saint Antoine Research Center, Paris), V. Navarro (Salpêtrière Hospital & Paris Brain Institute, Paris) : tRreg protection of seizure propagation zones In temPoral Lobe EpilepsY (RIPLEY) ; ANR-23-CE14-0052.
- Tronche (Neuroscience Paris Seine), D. Blum (Lille Neuroscience & Cognition) : Stress signaling in microglia: behavioral, functional, and molecular consequences (MicroGlioStress) : ANR-23-CE14-0010.
- Collaboration with J. Perroy (IGF), ANR-Glyphore: impact of dietary glyphosate on brain functions.
- Collaboration with C. Jopling (IGF), ANSES OptoFish: examines the impact of environmental contaminats using zebrafish models.



